Configuring Alerts
Alerts allow your trap to notify you when specific conditions are met. When an operator executes your trap's shouldAlert function and it returns true, an alert is sent to your configured notification channels (Slack, or webhooks).
How Alerts Work
- Operator Execution: Operators execute your trap's
shouldAlertfunction on every new block - Alert Condition: If
shouldAlertreturnstrue, the operator sends alert data to the Drosera alert server - Notification Delivery: The alert server forwards the alert to your configured destinations (Slack channels, webhooks)
- Alert Management: Alerts can be created, updated, and deleted without making any on chain changes.
Implementing shouldAlert in Your Trap
Your trap contract must implement the shouldAlert function which receives an array of collected data and returns a boolean along with custom alert data:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity ^0.8.12;
import {Trap} from "drosera-contracts/Trap.sol";
struct CollectOutput {
uint256 liquidity;
uint256 blockNumber;
}
struct AlertOutput {
bool shouldAlert;
bytes alertData;
}
contract MyTrap is Trap {
function collect() external view override returns (bytes memory) {
// Collect data from the blockchain
return abi.encode(CollectOutput({
liquidity: getLiquidity(),
blockNumber: block.number
}));
}
function shouldAlert(bytes[] calldata data) external pure override returns (bool, bytes memory) {
if (data.length == 0) {
return (false, bytes(""));
}
// Decode the collected data
CollectOutput memory latestData = decodeAlertOutput(data[data.length - 1]);
// Define your alert condition
bool conditionMet = latestData.liquidity < 1000 ether;
if (conditionMet) {
// Return true and encode alert data
bytes memory alertData = abi.encode(latestData);
return (true, alertData);
}
return (false, bytes(""));
}
// Helper function to decode alert output in your trap
// You don't have to use this in your trap, it's essentially
// used to know how to decode the `alertData` bytes returned by
// `shouldAlert` in the alert server. You can use any function name you want.
function decodeAlertOutput(bytes calldata data) public pure returns (CollectOutput memory) {
return abi.decode(data, (CollectOutput));
}
function getLiquidity() internal view returns (uint256) {
// Your liquidity logic here
return 1000 ether;
}
}Key Points
shouldAlertreceives an array of collected data (from yourcollectfunction)- Return
(true, alertData)when you want to trigger an alert - Return
(false, bytes(""))when no alert is needed - The
alertDatawill be decoded and sent to your configured channels
Configuring Alerts in drosera.toml
Alerts are configured under the [traps.<trap_name>.alert] section in your drosera.toml:
[traps.my_trap]
path = "out/MyTrap.sol/MyTrap.json"
cooldown_period_blocks = 32
block_sample_size = 10
[traps.my_trap.alert]
title = "Low Liquidity Alert"
severity = "high"
enabled = true
labels = { "pool" = "ETH/USD", "description" = "Liquidity below threshold" }
alert_output_sig = "decodeAlertOutput"
webhook = { webhook_url = "https://your-server.com/webhook" }Alert Configuration Fields
Required Fields
title(string): A descriptive title for your alertseverity(string): One oflow,medium,high,criticalenabled(boolean): Whether the alert is active
Optional Fields
-
labels(map): Key-value pairs for categorizing alertslabels = { "environment" = "production", "severity" = "critical" } -
alert_output_sig(string): The function name used to decode alert data- Example:
"decodeAlertOutput" - Must match a function in your contract that can decode the
alertDatareturned byshouldAlert
- Example:
-
users(array): User addresses that can view and manage alerts in the Drosera web app https://app.drosera.io/alerts. Needed for configuring Slack alerts.users = [ { address = "0x1234..." }, { address = "0x5678..." }, ] -
slack(object): Slack channel configurationslack = { slack_channel = "#drosera-alerts" } -
webhook(object): Webhook endpoint configurationwebhook = { webhook_url = "https://your-server.com/webhook", webhook_headers = { "Authorization" = "Bearer token" } }
Severity Levels
Severity levels help categorize and prioritize alerts:
low: Information that doesn't require immediate actionmedium: Important information that should be reviewedhigh: Issues that need prompt attentioncritical: Urgent issues requiring immediate action
The severity is displayed in Slack alerts with emoji indicators (👋 ⚠️ ❗ 🚨) and included in webhook payloads.
Setting Up Slack Alerts
1. Configure in drosera.toml
[traps.my_trap.alert]
title = "Low Liquidity Alert"
severity = "high"
enabled = true
alert_output_sig = "decodeAlertOutput"
users = [
{ address = "0x1234567890123456789012345678901234567890" }
]
slack = { slack_channel = "#drosera-alerts" }2. Deploy your trap
drosera applyThis will deploy your trap and create the alert configuration in the alert server.
3. Install Slack App
You need to install the Drosera Slack app in your workspace and authorize the alert server to post messages:
- Navigate to https://app.drosera.io/alerts
- Connect the wallet that owns the configured user address.
- Follow the instructions to authenticate with the Drosera app.
- Click on the "Install Slack App" button on the associated alert.
- Follow the instructions to install the app in your workspace and select the channel you want to send alerts to.
After installing the app, you will be redirected to the alerts page with the app installed.
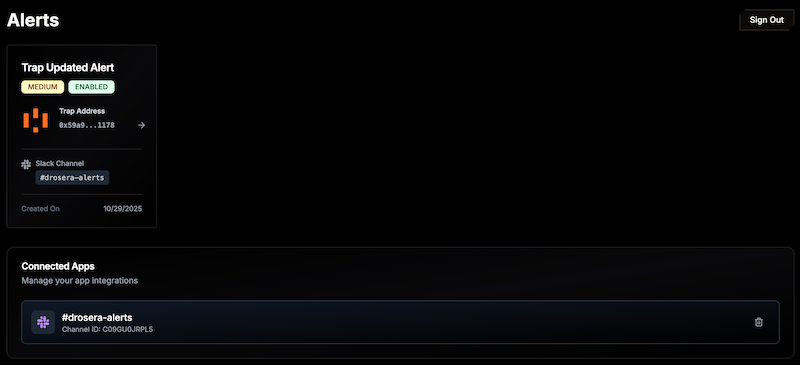
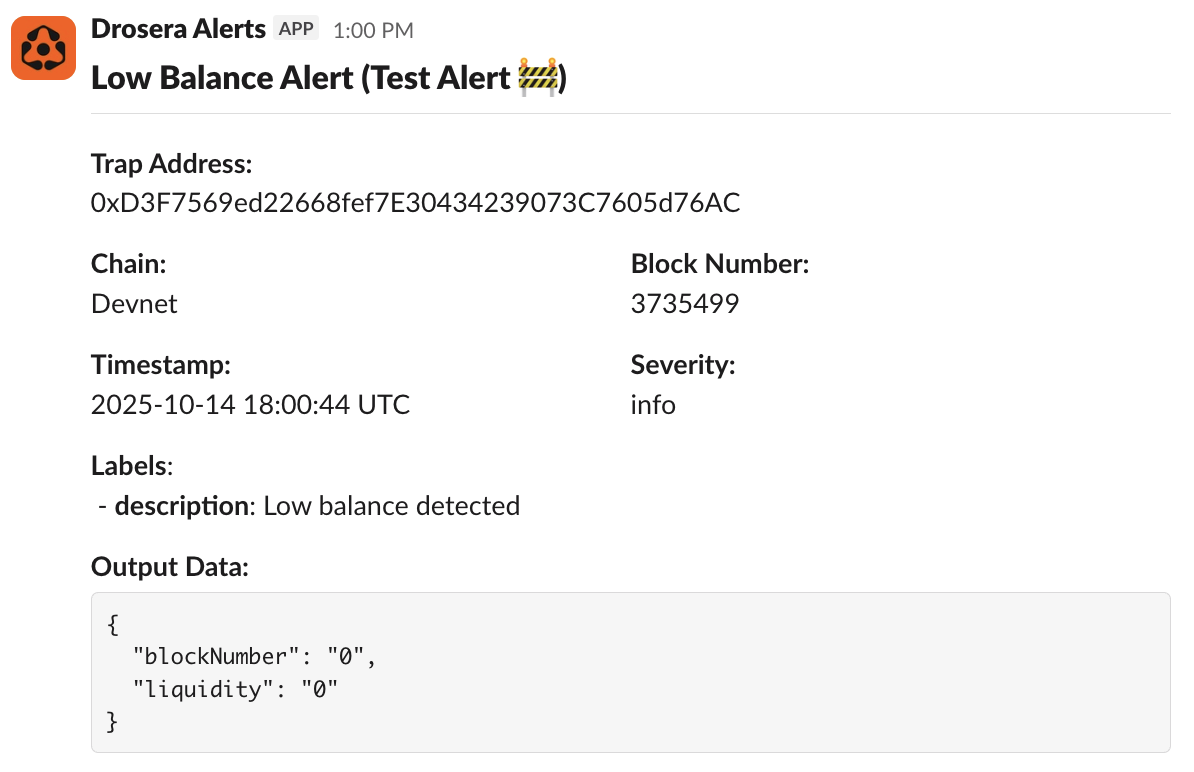
4. Slack Alert Format
When an alert is triggered, Slack will receive a message with:
- Header: Alert title with severity emoji
- Trap Address: The contract address of your trap
- Chain: Network name (Ethereum, Localnet, etc.)
- Block Number: Block where the alert was triggered
- Timestamp: When the alert was sent (UTC)
- Severity: Alert severity level
- Labels: Optional key-value pairs
- Output Data: Decoded alert data from your
shouldAlertfunction
Example Slack message:
Setting Up Webhook Alerts
Webhooks allow you to send alert data to any HTTP endpoint. This is useful for integrating with external monitoring systems, databases, or custom alert handlers.
1. Configure Webhook in drosera.toml
[traps.my_trap.alert]
title = "Low Liquidity Alert"
severity = "high"
labels = { "pool" = "ETH/USD", "description" = "Liquidity below threshold" }
alert_output_sig = "decodeAlertOutput"
enabled = true
webhook = {
webhook_url = "https://your-server.com/api/alerts",
webhook_headers = { "Authorization" = "Bearer your-token" }
}2. Deploy your trap
drosera applyThis will deploy your trap and create the alert configuration in the alert server.
3. Webhook Payload
Your webhook endpoint will receive a POST request with the following JSON payload:
{
"trap_address": "0x1234567890123456789012345678901234567890",
"block_number": 12345678,
"owner": "0xabcdefabcdefabcdefabcdefabcdefabcdefabcd",
"title": "Low Liquidity Alert",
"severity": "high",
"chain_id": 1,
"labels": {
"pool": "ETH/USD",
"description": "Liquidity below threshold"
},
"response_data": {
"liquidity": "500000000000000000",
"blockNumber": "12345678"
}
}3. Creating a Webhook Handler
Example webhook handler in Node.js:
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
app.post('/api/alerts', (req, res) => {
const {
trap_address,
block_number,
title,
severity,
chain_id,
labels,
response_data
} = req.body;
console.log(`Alert: ${title}`);
console.log(`Severity: ${severity}`);
console.log(`Trap: ${trap_address}`);
console.log(`Block: ${block_number}`);
console.log(`Labels:`, labels);
console.log(`Data:`, response_data);
// Your alert handling logic here
// - Index the alert in your monitoring system
// - Send an email to the alert owner
// - Trigger an automation
// - etc.
res.status(200).json({ received: true });
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Webhook server listening on port 3000');
});Webhook Security
For production webhooks, you should:
- Verify the sender: Use signature verification to ensure requests are from the alert server
- Use HTTPS: Always use
https://URLs - Validate data: Check that the payload matches your expected structure
- Rate limit: Implement rate limiting to prevent abuse
Example with signature verification:
webhook = {
webhook_url = "https://your-server.com/api/alerts",
webhook_headers = {
"X-API-Key" = "your-secret-key",
"Authorization" = "Bearer {{env.WEBHOOK_SECRET_KEY}}" # if using drosera.toml.j2
}
}Understanding Alert Output Signatures
The alert_output_sig field tells the alert server how to decode the alertData bytes returned by your shouldAlert function.
Simple Types
For a function returning a single uint256:
// In your trap contract
function decodeAlertOutput(bytes calldata data) public pure returns (uint256) {
return abi.decode(data, (uint256));
}Output JSON:
"500000000000000000"Structs
For returning custom structs:
struct CollectOutput {
uint256 liquidity;
uint256 blockNumber;
}
function decodeAlertOutput(bytes calldata data) public pure returns (CollectOutput memory) {
return abi.decode(data, (CollectOutput));
}Output JSON:
{
"liquidity": "500000000000000000",
"blockNumber": "12345678"
}Multiple Parameters
For returning multiple values:
function decodeAlertOutput(bytes calldata data) public pure returns (uint256, address) {
return abi.decode(data, (uint256, address));
}Output JSON:
["500000000000000000", "0x1234567890123456789012345678901234567890"]Labeling Alerts
Labels are key-value pairs that help categorize and filter alerts:
labels = {
"environment" = "production",
"component" = "liquidity-monitor",
"pool" = "ETH/USD",
"description" = "Liquidity below minimum threshold"
}Labels are included in:
- Slack messages
- Webhook payloads
- Alert queries
You can use labels to:
- Group related alerts
- Filter alerts in monitoring systems
- Add context to alert notifications
- Enable alert routing based on tags
Enabling and Disabling Alerts
Alerts can be enabled or disabled by modifying the drosera.toml file:
# Enable alerts
[traps.my_trap.alert]
enabled = true
# Disable alerts
[traps.my_trap.alert]
enabled = falseWhen enabled = false:
- The trap continues to run normally
- The alert server won't send alert data to the alert server
- No notifications will be sent
When enabled = true:
- Operators will call
shouldAlertand send alert data when it returnstrue - Notifications will be sent to configured channels
After modifying the drosera.toml file, you need to run the drosera apply command to apply the changes.
Multi-Channel Alerting
You can configure multiple notification channels for a single alert:
[traps.my_trap.alert]
title = "Critical System Alert"
severity = "critical"
enabled = true
labels = { "severity" = "critical" }
alert_output_sig = "decodeAlertOutput"
# Send to Slack
slack = { slack_channel = "#critical-alerts" }
# Send to webhook
webhook = { webhook_url = "https://your-server.com/alerts" }All configured channels will receive the alert simultaneously.
Testing Alerts
Dry Run
Use the dry run command to test your trap's alert logic without actually sending notifications:
drosera dryrun --trap-name my_trapThis will show you:
- Whether
shouldAlertreturnstrueorfalse - What data would be sent if an alert was triggered
- How the alert data would be decoded
Test Alert
Once your trap is deployed and configured, you can send a test alert:
drosera send-test-alert --trap-name my_trapThis sends a test notification to verify your Slack or webhook configuration is working correctly.
Managing Alert Configuration
Creating Alerts
When you deploy a new trap with alert configuration:
drosera applyThis will:
- Deploy your trap contract
- Create the alert configuration in the alert server
- Link users, Slack channels, and webhooks to the alert
Updating Alerts
To update an existing alert configuration:
-
Modify the alert section in your
drosera.toml:[traps.my_trap.alert] title = "Updated Alert Title" # Changed severity = "critical" # Changed enabled = true -
Apply the changes:
drosera apply
Deleting Alerts
To remove an alert configuration:
-
Remove the alert section from
drosera.toml:# [traps.my_trap.alert] # Commented out or deleted -
Apply the changes:
drosera apply
Best Practices
Alert Conditions
- Keep alert conditions specific and actionable
- Avoid alerting on temporary or expected conditions
function shouldAlert(bytes[] calldata data) external pure override returns (bool, bytes memory) {
if (data.length < 2) {
return (false, bytes(""));
}
CollectOutput memory previous = abi.decode(data[data.length - 2], (CollectOutput));
CollectOutput memory current = abi.decode(data[data.length - 1], (CollectOutput));
// Only alert if condition persists across multiple blocks
bool shouldTrigger = current.liquidity < threshold && previous.liquidity < threshold;
if (shouldTrigger) {
return (true, abi.encode(current));
}
return (false, bytes(""));
}Severity Levels
- Use appropriate severity levels for the impact of the condition
- Reserve
criticalfor truly urgent issues - Use
lowfor informational alerts
Labels
- Use consistent label keys across related traps
- Include relevant context (pool names, contract addresses, etc.)
- Keep label values descriptive but concise
Webhook Reliability
- Implement retry logic in your webhook handler
- Use idempotency keys to handle duplicate alerts
- Log all alert payloads for debugging
Troubleshooting
Alert Not Triggering
- Check
enabled: Ensureenabled = truein your config - Verify
shouldAlertlogic: Use dry run to test the condition - Check operator status: Ensure operators are running and watching your trap
- Review trap configuration: Confirm the trap is deployed correctly
Slack Not Receiving Alerts
- Check Slack app installation: Ensure the Drosera app is installed
- Verify channel name: Use the exact channel name including
#(private channels do not use#)
Webhook Not Receiving Alerts
- Test endpoint: Verify your webhook URL is accessible
- Check headers: Ensure required headers are configured correctly
- Review firewall rules: Confirm the alert server can reach your endpoint
- Validate SSL certificate: For HTTPS endpoints, check certificate validity
Incorrect Decoded Data
- Verify
alert_output_sig: Ensure it matches a public function in your contract that can decode thealertDatabytes returned byshouldAlert - Check struct encoding: Confirm the struct matches the encoded data
- Review encoding in contract: Verify how data is encoded in
shouldAlert
Complete Example
Here's a complete example of a trap with alert configuration:
Trap Contract
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity ^0.8.12;
import {Trap} from "drosera-contracts/Trap.sol";
struct CollectOutput {
uint256 balance;
uint256 timestamp;
uint256 blockNumber;
}
contract BalanceMonitor is Trap {
uint256 public constant LOW_BALANCE_THRESHOLD = 1000 ether;
function collect() external view override returns (bytes memory) {
return abi.encode(CollectOutput({
balance: address(this).balance,
timestamp: block.timestamp,
blockNumber: block.number
}));
}
function shouldAlert(bytes[] calldata data) external pure override returns (bool, bytes memory) {
if (data.length == 0) {
return (false, bytes(""));
}
CollectOutput memory latest = decodeAlertOutput(data[data.length - 1]);
if (latest.balance < LOW_BALANCE_THRESHOLD) {
return (true, abi.encode(latest));
}
return (false, bytes(""));
}
function decodeAlertOutput(bytes calldata data) public pure returns (CollectOutput memory) {
return abi.decode(data, (CollectOutput));
}
}Configuration
[traps.balance_monitor]
path = "out/BalanceMonitor.sol/BalanceMonitor.json"
block_sample_size = 5
[traps.balance_monitor.alert]
title = "Low Balance Warning"
severity = "high"
enabled = true
labels = {
"type" = "balance-monitor",
"threshold" = "1000 ETH"
}
users = [
{ address = "0x1234567890123456789012345678901234567890" }
]
alert_output_sig = "decodeAlertOutput"
# Multiple notification channels
slack = { slack_channel = "#finance-alerts" }
webhook = {
webhook_url = "https://your-server.com/alerts",
webhook_headers = { "Authorization" = "Bearer secret-token" }
}Deploy and Apply
# Deploy the trap
drosera apply
# Test the alert logic
drosera dryrun --trap-name balance_monitor
# Send a test alert
drosera send-test-alert --trap-name balance_monitorThis configuration will:
- Monitor the contract balance on every block
- Alert when balance drops below 1000 ETH
- Send notifications to Slack, webhook, and specified users
- Include decoded balance data in all alerts
